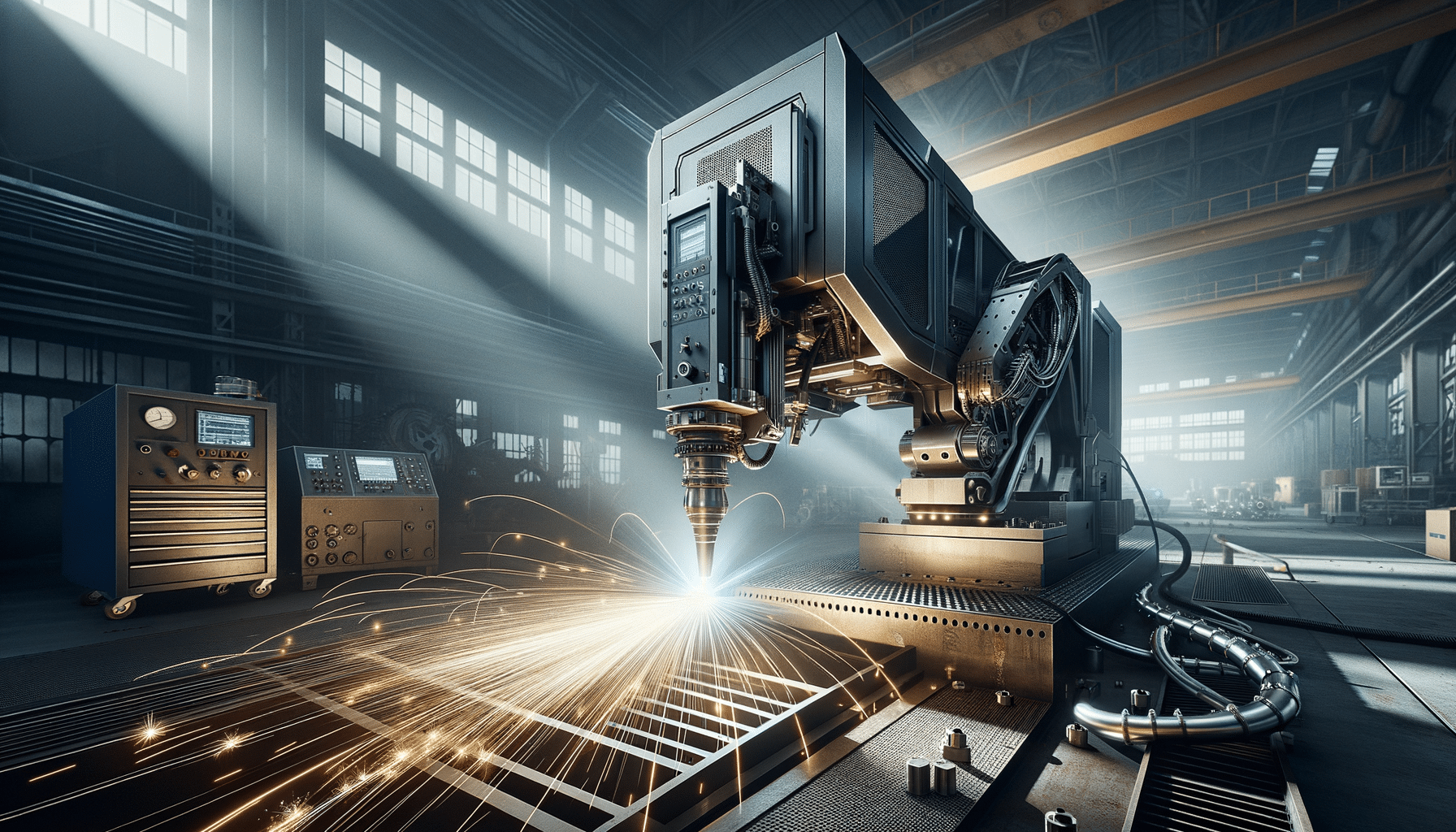
Laser Welding Machines: How They Work and When They Are Used
Introduction to Laser Welding Machines
Laser welding machines have become an integral part of modern manufacturing, particularly in industries that require precision and efficiency. Unlike traditional welding methods, which often involve a manual process and can result in inconsistencies, laser welding utilizes a concentrated beam of light to join materials with exceptional accuracy. This method is increasingly favored in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing due to its ability to produce high-quality welds with minimal heat distortion.
The relevance of laser welding machines today lies in their ability to meet the demands of high-volume production with precision and speed. As industries continue to evolve, the need for advanced welding technologies that can handle complex geometries and a wide range of materials is more critical than ever. Laser welding machines address these challenges by providing a versatile solution that ensures both efficiency and quality.
How Laser Welding Machines Work
The operation of laser welding machines is grounded in the principles of laser technology. A laser, which stands for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation,” produces a highly focused beam of light that can be directed with precision. When this beam is applied to the surfaces of metal parts, it generates intense heat that melts the material, allowing for a seamless joint to form upon cooling.
There are several types of laser welding processes, including:
- Pulsed Laser Welding: Ideal for thin materials and applications requiring minimal heat input.
- Continuous Wave Laser Welding: Suitable for thicker materials and high-speed applications.
- Hybrid Laser Welding: Combines laser welding with traditional methods to enhance penetration and speed.
Each of these processes offers distinct advantages, depending on the specific requirements of the task. The choice of laser type, such as CO2, Nd:YAG, or fiber lasers, also influences the machine’s performance and suitability for different materials and thicknesses.
Applications of Laser Welding Machines
Laser welding machines are employed across a myriad of industries, each with unique demands and challenges. In the automotive industry, for instance, laser welding is used to assemble car bodies and components, where precision and strength are paramount. The aerospace sector benefits from laser welding’s ability to join lightweight materials like titanium and aluminum, which are essential for building efficient aircraft.
In the field of medical device manufacturing, laser welding machines are used to produce intricate components that require high precision and cleanliness. This includes the assembly of surgical instruments and implantable devices, where even the smallest defect can have significant implications.
Beyond these industries, laser welding is also utilized in electronics, jewelry making, and even in the creation of art pieces, showcasing its versatility and adaptability to various applications.
Advantages of Laser Welding Machines
The advantages of using laser welding machines are numerous, making them a preferred choice for many manufacturers. Some of the key benefits include:
- High Precision: The focused laser beam allows for precise control over the welding process, reducing the risk of errors.
- Minimal Heat Affected Zone: Laser welding produces a small heat affected zone, minimizing distortion and preserving the integrity of the surrounding material.
- Versatility: These machines can weld a wide range of materials, including metals and plastics, and are effective for both thin and thick sections.
- Speed: Laser welding is a fast process, which can significantly increase production rates and reduce lead times.
- Automation: Laser welding machines can be easily integrated into automated production lines, enhancing efficiency and repeatability.
These advantages contribute to the growing adoption of laser welding machines in modern manufacturing, where quality and efficiency are of utmost importance.
Challenges and Considerations in Laser Welding
While laser welding machines offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges and considerations that must be addressed. The initial investment cost for laser welding equipment can be high, which may be a barrier for small to medium-sized enterprises. However, the long-term savings in efficiency and quality often justify this expenditure.
Another consideration is the need for skilled operators who understand the intricacies of laser welding technology. Proper training and experience are essential to maximize the capabilities of these machines and ensure safety standards are met.
Material compatibility is another factor, as not all materials respond equally to laser welding. Some metals may require pre-treatment or specific laser settings to achieve optimal results.
Overall, while laser welding machines offer outstanding potential, careful planning and investment in training and equipment are crucial to harnessing their full capabilities.
Conclusion: The Future of Laser Welding Machines
As industries continue to push the boundaries of innovation, the role of laser welding machines will undoubtedly expand. Their ability to deliver precision, efficiency, and versatility makes them an invaluable tool in modern manufacturing. While challenges exist, the ongoing advancements in laser technology promise even greater capabilities and applications in the future.
For businesses looking to improve their manufacturing processes, investing in laser welding machines can be a strategic decision that enhances product quality and production efficiency. As technology evolves, so too will the opportunities for laser welding, making it an exciting field to watch in the coming years.


